The Google Display Network is the largest contextual advertising network available on the Internet today.
It is the storehouse of millions of networks of millions of sites. Advertisers can show their display ads in multiple formats to a range of audiences worldwide using a wide variety of targeting methods.
We know it can be daunting, which is why we are ready to help if you need help to get started with the Google Display Network or want to speak to PPC marketers about developing a long-term growth plan.
At Pearl Lemon, we take the pressure off you and let our professional team of experts handle it for you.
Click here to book a call now!
Before you move on towards exploiting all GDN advertising has to offer, let’s discuss the types of advertising:
Types Of Advertising
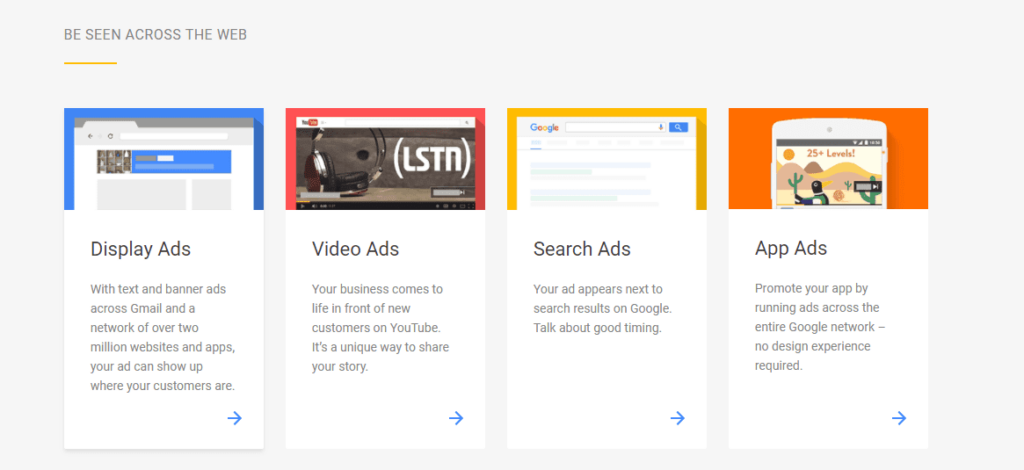
The mediums of putting out advertisements are endless, but strategically using the best-suited ones to deliver ads streamlines the elimination process.
Advertisers are frequently faced with the dilemma of whether to use display, native, or search ads or all three for their campaigns.
The following features show some of their distinctive aspects that you might want to consider to help you determine the best option for your goals.
Target
Search Ads
Through search ads, advertisers use keywords that describe the products they offer. So essentially, using SEO strategies such as using keywords make the ads easy for the Google crawlers to understand and index.
Search ads heavily rely upon waiting for customers to actively search for what advertisers are offering and involve many technical back-end SEO tactics.
Display Ads
Advertisers place display ads on websites that feature the interests of their target market.
It is a method of attracting the audience to a website, social media platform or another digital medium to take a specific action. They are targeted in their approach.
This method of targeting is usually achieved by screening the advertising campaign to target specific audiences by age, gender, etc.
Native Ads
Native ads very similar to display ads, but unlike them, native ads follow the natural form and function of the user experience in which it is placed.
In simpler terms, these advertisements stick to the genre of articles the viewer is currently reading. Thus, they maintain homogenous content.
So if you’re reading (or watching) a food blog and see a prompt for a restaurant offering deals, that’s an example of native advertising.
Content
Search and Display Ads
Search and display ads are more alike when it comes to content, which is crafted as an obvious advertisement aimed at a target market.
Since most of them are digitised, a significant amount of optimisation goes in, especially when using keywords.
So, suppose a jewellery company is using search or display advertising and targeting teenagers. In that case, their content is likely to be centred around current teenage styles and trends (such as custom-name necklaces, etc.)
Native Ads
Native advertising content, on the other hand, is a form of website advertising that is carefully integrated into the flow of a website’s editorial content.
As we mentioned before, they are not randomised and need to be aligned with the website’s topic or genre where the ad is being hosted.
In other words, the content for native ads is dependent on the platform they are being hosted on.
Form Of Display
Search Ads
Display Ads
On the other hand, displaying ads gives you a little more room for creativity by letting you create ads that exhibit various rich media such as videos and images or a fun mix of both.
They are usually dynamic and use different mediums, and if taken advantage of (with respect to their scope), are advantageous.
Native Ads
Native ads use rich media too. Except, the main difference lies in how native ads are made to fit seamlessly into websites to look more “authentic” in an attempt not to interrupt the natural flow.
As you can imagine, the possibilities for putting out a well-rounded and strong advertisement are boundless.
Qualified marketers and advertisers can say precisely when and where certain commercials are best used for which campaigns.
This might be whether they’re for B2C or B2B advertising, because of their great understanding of what display advertising is.
The website-based advertising banners or advertisements inserted in specific sections of websites are designed to target the same demographic with the product it offers.
To attract the attention of website users, these advertisements may include text, advertising images, videos, sounds, animation or other highly interactive elements.
This guide’s focus will be with Display Advertising and how you can use Google’s platform to expand your reach and potentially sell out.
Using Google Display Network To Publish Your Ads
It was in the year 1993 that web advertising was born. It was the very first time Global Network Navigator sold a display ad.
Global Network Navigator was the first-ever commercial web publication that offered clickable ads and is now considered the first commercial website in history.
So, what is Google Display Network (GDN?)
GDN is a group of more than 2 million websites, videos, and apps where your Google Adwords (more commonly called Google Ads) can appear.
So essentially, when you launch a Google Ads campaign, your ads can be launched into the GDN for higher impressions if you choose to do so.
Advertising on Google Display Network translates to pushing your ad content out to over 2 million sites. In turn, these reach over 90% of people on the Internet who are shown your ads, articles, videos, or websites that consumers browse.
Display Advertisement
Contrary to its name, the display network allows for a range of ad formats, including text and video, as well as traditional image advertisements that are extremely popular around the internet.
Different types of ads allow various targeting and duplication styles to come together. This offers the best possible conditions for related traffic, conversions and revenue to be powered.
Google Search vs. Display Network
When using Google’s Display Network, you need different goals than when using the search network; when posting on Google Ads. Let’s describe those instances of usage and expectations.
The biggest differentiator is the fact that the primary focus of the customer is the content of the website itself. The display ad has an indirect, secondary role in the viewer’s appeal to the website.
Marketers hope that the potential consumer will see their GDN ad along their journey to serve another purpose.
That makes the intent of the advertiser different, or more diverse from when an ad appears for a high-intent search term at the top of a Google results page.
It should be no surprise that the click-through rate and conversion rate for GDN are below 1%.
There are a number of targeting options outside of keywords that span millions of websites across a network, unlike with Google. Via website placements, you can reach the majority of internet users.
With strict targeting requirements, your number-one objective with GDN is to find the right audience size.
With stronger, more appropriate targeting, there are many ways of approaching this network. Ultimately, remarketing is limitless – but beyond the Google Ads network, it requires audience growth.
Types of Display Advertising
Text ads
Image ads
A static image that would fill the entire ad block on the website it appears upon.
Image ads allow for custom imagery, layouts and background colours on image ads.
Video ads
Video ads have become more popular primarily due to YouTube sponsorship and ad opportunities which are included on the Display Network.
You can now use video content in ads across the display network.
Display and Search Ads
As we mentioned before, search ads show up to potential customers the moment that they start looking on Google for what you offer. Whereas, Display ads show up while people are visiting sites across the Google Display Network.
Unlike search ads, display ads are not very targeted since they do not reach those who are actively searching for what you offer.
However, you’re still introducing your business to a relatively dilute yet broad audience who is likely to be interested in your products or services.
This may help you to reach a larger or completely new audience than simply through direct searches.
Why Google Display Network
The convenience of the Google Display Network has increasingly contributed to reaching more target customers or website visitors.
This is mainly because of the ease-of-use of Google Ad launch campaigns, which we will explore soon.
Below, we will assess why GDN can be really great for your business:
Cost-Effective
Unlike most ad setups, Google Ads offers Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising where you only pay for each click that your Google Ad receives.
As you can imagine, this gives you a significant upper hand as you only pay for leads or potential customers without committing to an overall price.
Google has provided in-depth advice on how you can effectively budget your advertising which you can find here.
Your ads usually are powered through bid strategies which are heavily reliant upon your goals.
Your campaign’s cost is very likely to skyrocket if you don’t manage your campaign carefully because of the high average cost.
Moreover, the competition within GDN is a massive battleground. Ranking or topping Google’s search results is going to be a challenge. This is because it would be very expensive in some cases to bid for your brand using expensive keywords.
Different people have different expectations about what they wish to achieve from these ads. So, ideally, these are the generic bidding strategies we would recommend:
- If your goal is to ensure direct customer action on your site using conversion tracking, Smart Bidding is the one for you.
- If your goal is to generate traffic to your website, focusing on cost-per-click (CPC) bidding would be ideal for you.
- If your strategy is to increase brand awareness, focusing on impressions, cost-per-thousand viewable impressions (vCPM) bidding to put your message in front of customers is recommended.
- Cost-per-view (CPV) or cost-per-thousand-impressions (CPM) bidding would be ideal for video ads where you want to increase views or interactions with your ads.
- At the same time, if you run video ads, and your goal is to increase product or brand consideration, you can use cost per view (CPV).
Google Ads’ bid simulator is an effective tool to help you to see how different bids might change your ads’ weekly performance which is another feature worth considering.
Of course, there are ads that may require you to choose between multiple bidding strategies. But a strong sense of what you wish to achieve will make all the difference.
When your objectives have been determined, come up with tactics to help you accomplish those goals and make the most of your budget.
Try Smart campaigns, where you set a maximum monthly budget. If you’re new to Google Advertising, then rely on Google to automatically change ad bids to drive better results.
When you become a professional advertiser, you can explore bidding techniques like Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) or Cost Per Mille (CPM).
For an in-depth understanding of how Google’s bidding system works, check this page out.
Chances of Greater Impressions
Display Ads can be scaled dramatically to a wide range of audiences since every aspect of video ads can be managed by targeting through keywords, placements, interests, topics and remarketing.
When compared with search ads, the extension of optimisation is relatively limited. Because the customers need to search to be advertised on a product or service, a low number of conversions or leads are observed.
To study your impressions and how much exposure your ads are getting, connecting your Google Ads and Analytics accounts may be helpful.
Google Ads reveals how many times your advertisements have been viewed in searches (called “ad impressions”) and when they have been clicked.
Unfortunately, it does not give you insights into whether these experiences make any actual contribution to your website conversions.
In this case, use the free Google Analytics tool if you want to monitor your conversions (purchases, calls, form submissions) or other actions that your customers take on your site.
Likewise, Google Analytics will inform you when after clicking a specific ad, visitors leave your website immediately.
This is a very insightful indicator which might mean that the bounce rates your website is experiencing are due to the inaccuracy or irrelevance of the keywords you’ve opted for.
In this instance, you might choose to experiment with different keywords, instead of sticking to the same few that aren’t bringing about much (or any) conversions.
All in all, Google Analytics is an essential tool for all business owners and marketers. It’ll do you good to regularly review the data in your Google Analytics account to study your web performance with respect to the ads you’ve paid good money for.
Improve the relevancy of your landing page or keywords using this data. In turn, this could raise your ad’s Quality Score.
Quality scores show an estimate of how relevant your ads, keywords, and landing page are to a person who sees your ad. Higher Quality Scores typically lead to lower costs and better ad positions.
Remarketing
Remarketing involves showing paid ads to users based on their past activity on your website.
Ads on GDN have the exceptional ability to follow previous visitors and show ads to them across Google’s large network of partner sites. These include Youtube, Facebook or any other website your previous visitors browse.
In many ways, the remarketing feature allows past visitors to reassess the ads and develop an interest which was initially absent.
For example, if you very recently shifted to a vegan diet, advertisements of vegan restaurants or recipes would interest you now a lot more now than when would when you were still a non-vegetarian (or followed any other non-vegan diet).
Remarketing helps marketers complete the paid search engagement loop where you keep past users active on your website at all times.
Some of the most common remarketing audiences include:
- General website visitors
- Users who have submitted a form
- Users who have downloaded content
- Users who have viewed specific product pages
- Users who have signed up for an account or trial offer
- Users who have completed a transaction or purchased a product
- Users who have begun any of the above actions but abandoned the page before completing it
Some businesses prefer to focus only on remarketing because reaching users already familiar with your brand drives leads and sales for the most affordable cost.
Other firms, however, are not focused on encouraging returning customers as much as on raising awareness of their goods and services.
It all comes down to the marketing goals of the business.
Types of Display Advertising Formats on the GDN
Google Ads is the largest Display Advertising provider.
One of Google Ads’ biggest benefits is that it does not have a limited target system of pushing out ad content just on Google, but also reaches users who search with other search engines such as DuckDuckGo, Go, Daddy, Yahoo and many more.
Search engine advertising also covers YouTube, which ranks as the second-largest search engine.
Now, Google Display Network (GDN) allows advertisers to choose the ad formats they want to use.
These formats may be based on website context (native ads) or target audience.
As the Google ad network grows, marketers need to realise how important Display Advertising is (especially for small business advertising efforts) in promoting their companies.
Due to this, the scope for creating display ads using Google gives you a wide variety of formats.
Text Ads
Text Advertisements consist of two lines of text and a headline. It enables marketers to build a wide variety of advertising and see what is most powerful and clickable.
These are the types of standard text ads:
Full Slot Ads
These ads use the entire space of the ad post.
Partial Slot
Magazine-Style Ads
Magazine style ads work only on the Display Network, as the network ensures consistency for layout, magazine-style text, fonts and colours.

Native Text Ads
Native text ads incorporate the usual look and feel of a publisher’s site. Having a Google+ Accounts logo and other third-party image sources can help increase this ad type’s performance.
Rich Media Text Ads
Rich media text ads work with images. They increase performance; and logos from Google+ Accounts and other third-party sources may be used.
Image Ads
Image ads contain set photos that take up the entire ad space on a website. Use caution to ensure that standards are followed, as disapproval is subjected to advertisements that breach policies.
Video Ads
Video ads are common because of the accessibility of YouTube and its inclusion in the Display Network. YouTube videos are a great platform to place Google ads due to their increasing popularity as a search engine.
Rich Media Ads
Rich media ads include online video advertising, audio, animation or any platform that engages interaction with the audience such as a photo carousel.

Banner Ads
Instead of text-based or image-based, banner ads are usually a good mix of both and are a common form of online advertising.
The purpose of banner advertising is to promote a brand and/or to get visitors to go to the advertiser’s website from the host website.

Google Ads Guidelines
Google has a strict code of guidelines that extend across:
Prohibited content: Content you can’t advertise on the Google Network.
Prohibited practices: Things you can’t do if you want to advertise with Google.
Restricted content and features: Content you can advertise, but with limitations.
Editorial and technical: Quality standards for your ads, websites, and apps.
More generally, these are some ad-based guidelines:
- Image quality must be good, and in compliance with Google Ads quality expectations; the image must not be blurry.
- Information must not be irrelevant to the main subject of the ad. In other words, it must be related or have a strong correlation to the product or service being promoted.
- Content must not be misleading or have the potential to be loosely translated. The information must be exact, detailed, and the reader must be able to identify what is being advertised. There should be no site warnings or error messages, and ad images must only appear once.
- Ad images must not have adult content in their web banner design to keep ads safe for general users.
- The Interactive Advertising Bureau or IAB also has guidelines of its own for display ads that advertisers need to be aware of.
Display Ads Standard Banner Sizes
GDN provides numerous ad block sizes that are built to fit into a specific website layout for each ad block that appears on Google.
To be able to come out on various websites, it is good practice to produce Google display banners in different banner ad sizes.
If your online banner design does not come in different sizes, you may be restricting the audience you are able to attract.
There could be more chances of a higher click-through rate for banner web designs featuring photographs and rich media, but they have less exposure.
This is because a single block that has enough room for three text ads takes up one picture ad. Also, the cost of banner advertising will be higher for your ad to be displayed in this room.
These are the top-performing web banner sizes for Google display ads:
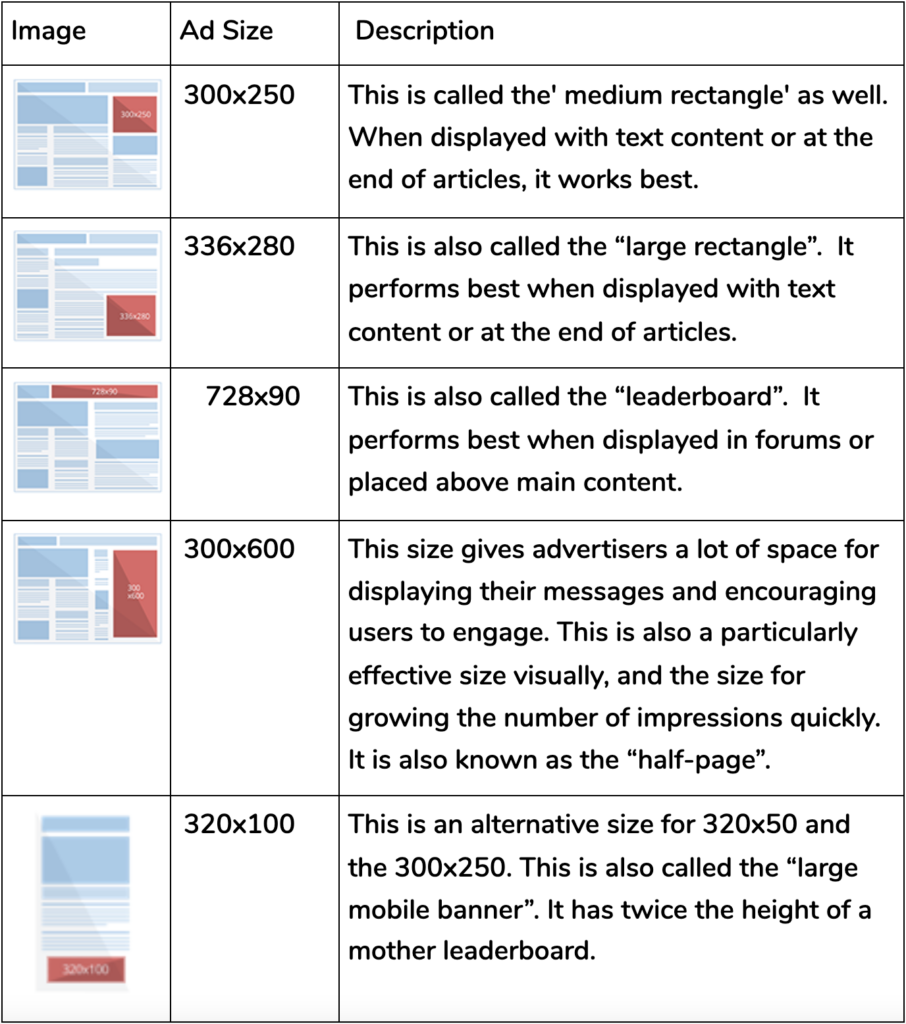
The best of the rest Google display ad sizes are:
250 x 250 – Square
200 x 200 – Small Square
468 x 60 – Banner
120 x 600 – Skyscraper
160 x 600 – Wide Skyscraper
970 x 90 – Large Leaderboard
320 x 50 – Mobile Leaderboard
Remember: Your Google banner advertising must have a simple call-to-action and a branding message. The banner ad design should always be appropriate for the website and relevant to its content.
Additionally, if you don’t have a lot of resources for creating display ads or banner design, you may use the Google Ads Display Ad Builder to make creative banner ads.
Now we have all the necessary apparatus and know-how for not only GDN but display advertising. We know what GDN is and the different ad types and sizes.
So let’s dive into how to use Google Display Network for businesses by launching a campaign together:
Creating An Ad
Before setting up your display ad campaign in Google Ads, there are a couple of important steps you need to pay attention to if you want to carry out a successful ad campaign.
First and foremost, before you create ads, you need to be clear on your objective.
What is the goal of these ads? How do you want your viewers to respond?
What do you want people to do when they see your ad? What does a conversion mean to you?
Where will you send traffic for them to convert?
Typically, most objectives align around setting up a landing page that is highly relevant to the ad that’s designed to convert.
When it comes to ad creation, display ads are one of the most popular formats because of the extent of customisation and viewer responsiveness they can create.
In the past, you would have to invest huge amounts of time on building ads of a variety of shapes and sizes. Fortunately, thanks to the clever robots at Google, we now have Responsive Display Ads.
Responsive display ads allow for the upload of a few pieces of content in the form of pictures or videos.
Add a copy of varying lengths, and you’re good to go. To ensure that your advertising will appear on as many pages as possible, Google can now automatically combine the various assets to fit all the necessary sizes and types of ads.
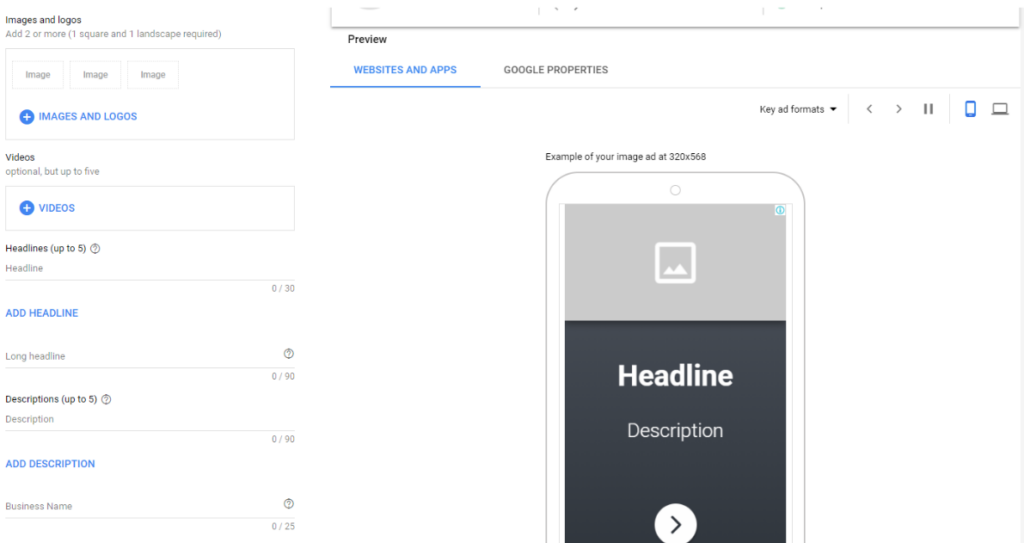
Targeting the Google Display Network allows you to set where or when your ad is seen based on your ideal audience’s characteristics, such as their personal preferences, age or gender.
This ensures that your ad can be seen on company-related websites, or to users who meet the particular requirements you have defined.
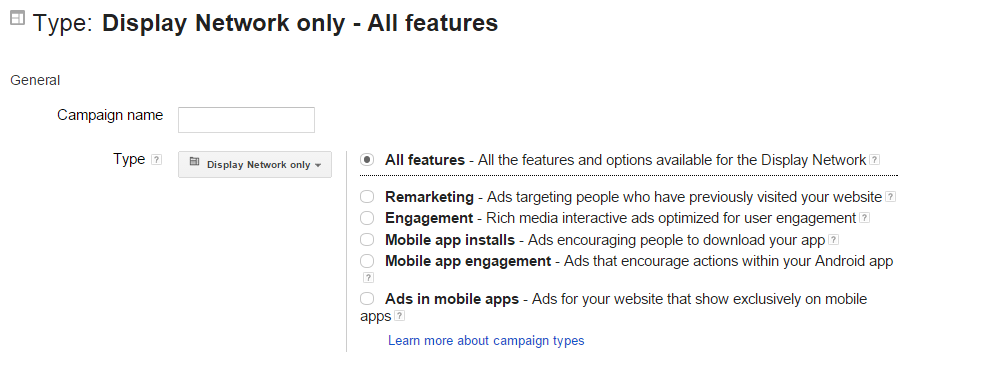
If you aren’t already running ads on the Google Display Network as part of your Google Ads account, here’s how you can do so:
- Log into your Google Ads account
- Click on “Campaigns,” and then “New Campaign”
- Select “Display Network only” as the campaign type
- Select a marketing objective
- Decide the location targeting for your campaign.
- Set your ad budget – this is how much you are willing to spend on your ads per day. Go for the Manual CPC to start, as this gives you more control. Then, you can always experiment as you learn the ins and outs. Start with a low bid and adjust it later (Google Ads gives you an idea of what you should be bidding).
- Pick Ad extensions, such as call extensions.
From here, select the types of Google Display Network targeting that you’d like to include as part of your campaign.
Specific Campaigning
The best practice to follow when running Google Advertising is to create campaigns based on your website’s various categories or sub-pages.
For example, if you want to run advertisements to promote your jewellery store, you wouldn’t want only to run one “Necklace” campaign.
Instead, it might look something like this in your campaigns:
Campaign: Bracelets
Campaign: Earrings
Campaign: Rings
So on and so forth.
This way, you can also set different budgets for each campaign.
Changing your expenses depending on your priorities (for example, putting more of your budget in the weeks leading up to Black Friday towards your “Bracelets” campaign).
Plus, you can present advertisements to potential customers that are more tailored to what they are looking for and take them to your site’s most important page.
Targeting on GDN
Targeting your advertisements to relevant audiences is one of the most important steps towards laying the groundwork for a successful campaign.
Your approach to GDN ads has to be somewhat different from those on the search network. When it comes to Google’s search network vs display network, users are in seek mode on the search network.
The display network, on the other hand, is more passive.
Therefore, since we are going to primarily discuss Display Ads in the Google Display Network, it is important to note that conventional advertising (usually search-based) won’t be the best option.
Essentially, in display advertising, you are showing ads on external sites that people are visiting for some other specific purpose.
This means that they aren’t specifically searching for your product or service, but are more likely to stumble across it as they’re exploring the internet.
Buyer Personas
Your game plan should start with a clear idea of realising WHO your ideal customers are, WHAT they are looking for and WHO they are looking for.
Otherwise, your ads won’t target the right people on the right websites, and your impressions are likely to be average with below average ROI.
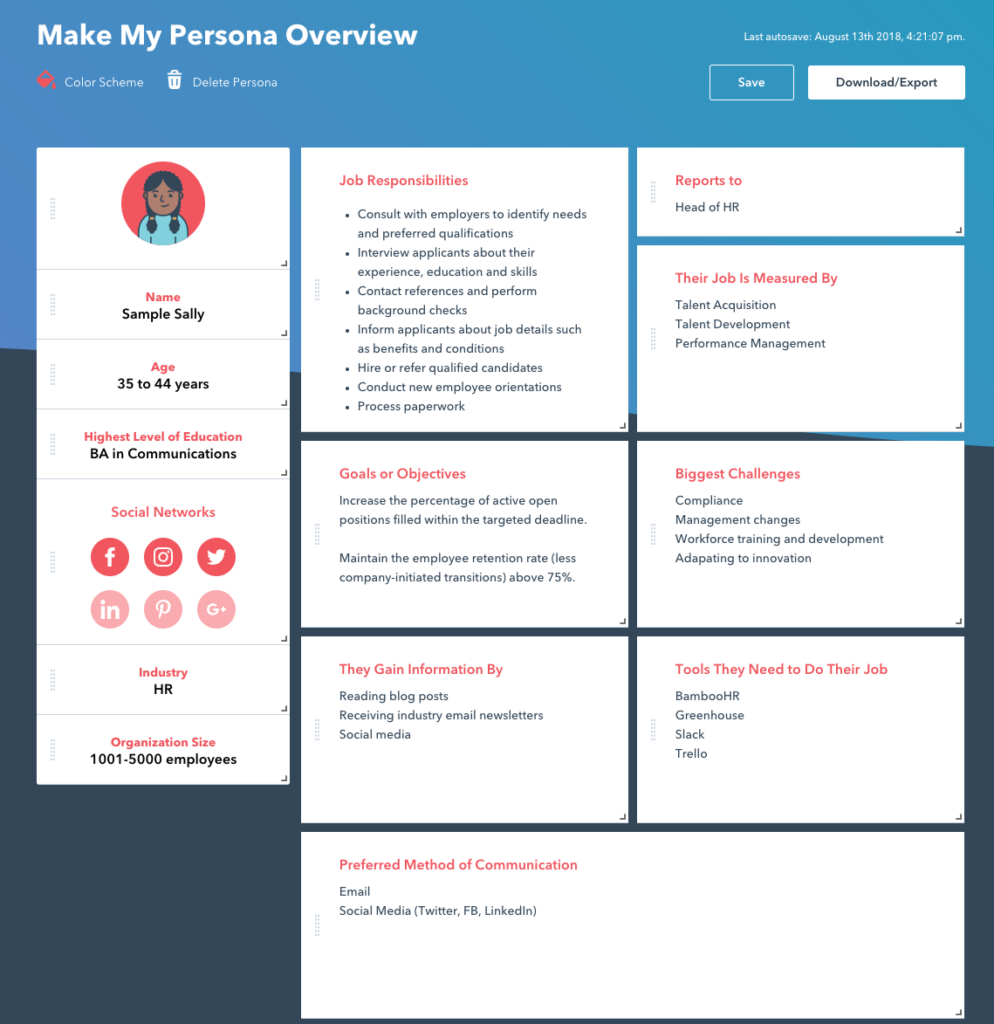
The best way to do this is to create buyer personas.
Buyer personas are a semi-fictional portrayal of your customers that categorise them based on their goals, pain points, objections, and other specific features of your ideal customer.
It is recommended that you do your research with your sales team, customer service team, and real-life customers to build personas that are as close to your potential customers as possible.
HubSpot’s Make My Persona is a great tool to consolidate your research and looks something like this:
Location
Showing the advertisements to the whole world is not the way to go if you have a local shop you want to get more local customers.
Alternatively, change your Google Ads targeting settings to display your ads only to individuals searching close enough to visit, or in other places that are important to your business.
You’ll spend your budget more wisely by doing this.
Location targeting can also be useful if your business serves customers outside of your country or globally.
Start by focusing your campaigns to a few places in which you think your company can do well, then keep an eye on your data to see where your traffic and conversions come from.
From there, maximise your ad budget and tailor your strategies to reach the best-performing regions or markets.
Interest targeting
Interest targeting is exactly what the name suggests – Google shows your ad to people who could potentially be interested in your products and services or those who engage in activities related to your business with respect to the data you have provided.
That is, if you sell maternity clothes and have added this information to be optimised to reach the target audience as a part of your campaign, Google will recommend this to moms and 25-40 age group women who are likely to have babies.
There are three categories of interest targeting you can choose from:
Audience targeting
Audience targeting allows for groups of users to be hit with ads based on their search history, interests and online behaviour.
In contrast to topic targeting, audience targeting groups users together and will display ads to these users on any website in the GDN, not just websites related to your product or service.
Affinity Audiences
This involves 80 separate categories, such as “sports fans”, “car enthusiasts” or “gamers”, focused on passions or hobbies. To advertise to one or more of these viewers, you can opt to screen your ads.
Custom Affinity Audiences
To narrow your targeting even further, create your own custom audience using keywords.
If you’re running ads for your newly founded bakery, you might use keywords such as “delicious mini cupcakes”, “birthday cakes”, and “easy to make recipes”.
When you set up your custom audiences, your ads will be shown to people visiting websites that contain these keywords.
At this point, it is important to consider using ‘long-tail keywords’ which are two to five-word phrases that your potential clients would type into a search engine when looking for you (or a business like yours.)
The drawback of using short keywords is that you tend to compete with billions of results.
For example, if you are an online e-commerce company selling headphones, you would want your searchers to type in “best headphones”.
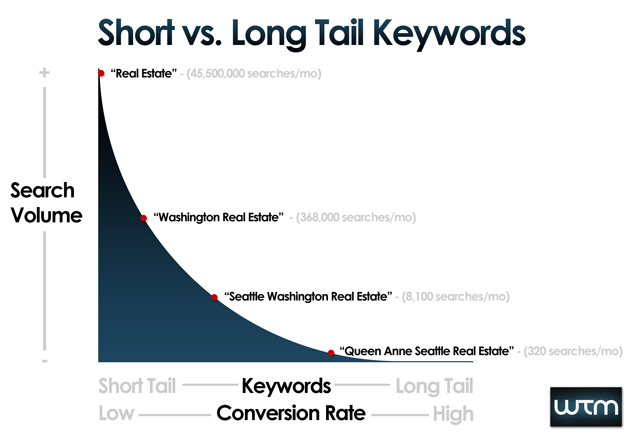
Photo credit: OnCrawl.com
However, adding such small keywords would generate millions of results and is very likely to rank your competitors higher who have been in the industry much longer.
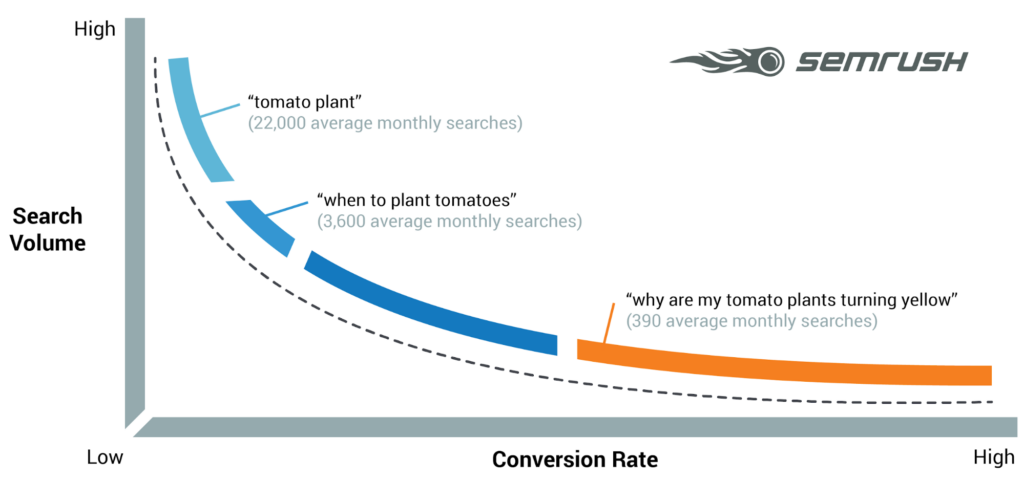
Photo Credit: semrush.com
This is why using longer keywords helps, as it allows you to boil your business down to certain key features such as “best headphones in London” or “best headphones under £15”.
The more targeted your keyword; the better. You’ll be able to attract the right audience and increase the chances of searchers clicking on your website from search results.
At Pearl Lemon, we have carefully selected the most effective ways to help you find the keywords for your website:
One of the best ways to rank high is to make sure you find the right keywords for your business and use these words in the text and other elements of your website.
Make a List
Photo Credit: searchenginejournal.com
Be Specific
While brainstorming, make sure you choose words that resonate with you, your business and the product or service it offers. Then, add your edge to it by making it trendy by means of using words like DYI.
If you run a local business, try adding a word that describes your location. This will help you target customers in your area and help the right people find your site.
Put yourself in your Customers’ Shoes
Play around with your perspective; instead of focusing on how your business should be presented, think about how you would like for it to be found.
Think about what your potential client would be looking for as they Google away on their computer or phone. For example, if you describe yourself as a “painter”, your target audience may be looking up the term “artist” more often on search engines.
Embrace Technology

Photo Credit: PageUp.com
These tools tell you exactly how many people are searching for specific terms each month. They also suggest terms to use and can tell you if a keyword is very competitive.
Google Keyword Tool
Apart from being a free SEO tool, Google Keyword Tool is owned by – Google. The only condition for using the tool is to run an AdWords campaign on Google.
If you do want to set up an AdWords campaign, however, you can then use the Keyword Tool to access monthly search numbers for a specific term nationwide, in your state, or even in your city.
Photo Credit: SirenSearch.com
Moz Explorer
While the Moz keyword tool only provides nationwide search data, it is excellent at recommending phrases that you may not have thought of. Its ability to suggest longer tail (more than 3-4 words) keywords with lower search volumes make it a great choice for small businesses.
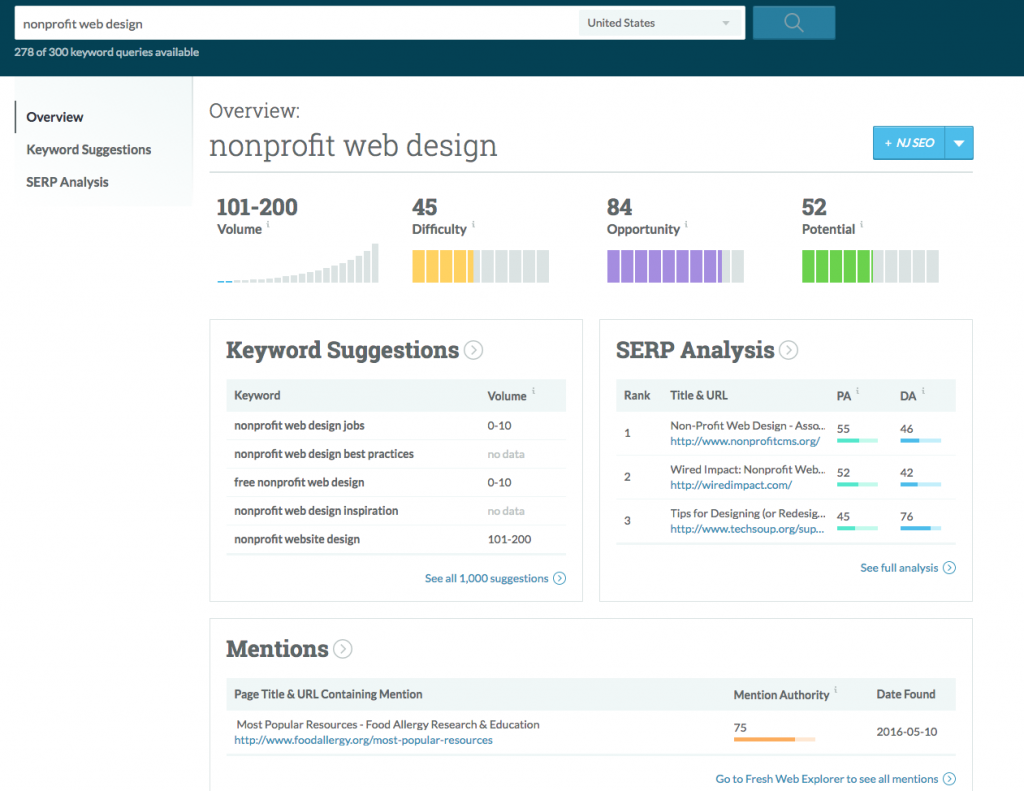
Photo Credit: HookAgency.com
Moz charges a monthly fee, but you can try it out free for 30 days. (And that should be more than enough time to get all the data you need).
SEMrush
In addition to getting keyword data, you can also use it to find out how your competitors are ranking. (Just enter their Domain, click on Organic Results and click on Positions) SEMRush only gives you one day to try out their tool and then you’ll have to pay.
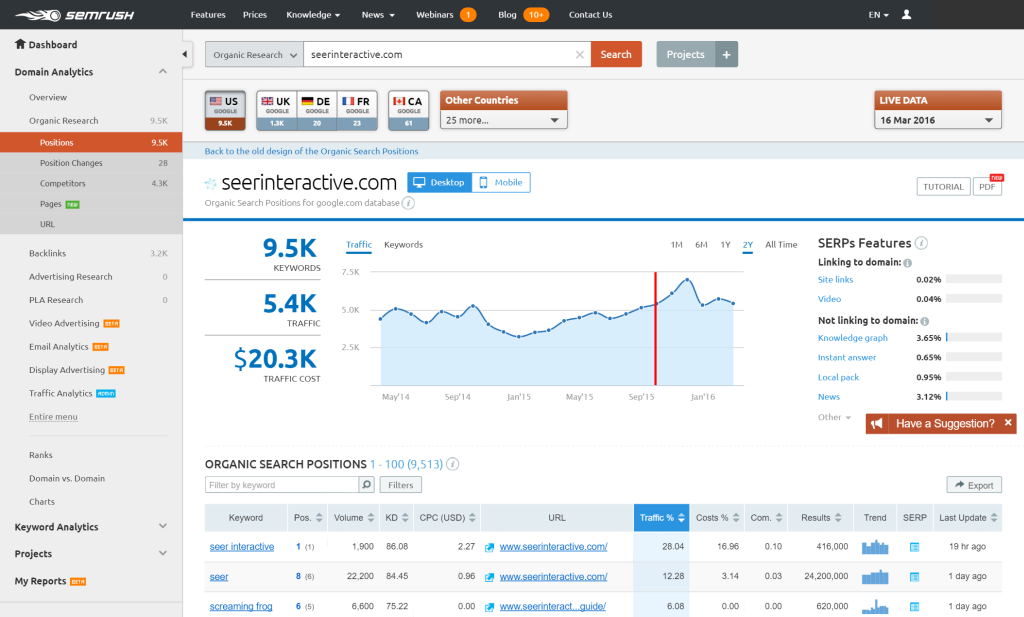
Photo Credit: SeerInteractive.com
Study your Competitors
While you may be an excellent baker based in the heart of New York City, phrases like “best NY baker”, or “the best New York bakery” are not likely to help you a lot in your ranking on the SERPs.
These are highly competitive terms, and it will be virtually impossible for a start-up bakery to show up on the first page of Google.
Find a niche instead – Look for your niche and try to find keywords that represent it.
Are you particularly talented when it comes to wedding cakes or small cupcakes? Or do you specialize in a certain type of cookie whose recipe was handed down to you through generations?
Add some specific adjectives to your key phrases, and you’ll boost your chances of ranking high.
Always choose Quality over Quantity
Choosing keywords that are highly competitive makes your SEO process very cumbersome. Instead, look for quality keywords that accurately and precisely describe what you do.
These long-tailed keywords ensure lower Cost Per Clicks (CPCs) when bidding on these keywords due to their low popularity.
Long-tail keywords are also more specific than short-tail keywords, and they attract searchers with a higher likelihood to buy, call or visit your business.
In-Market Audiences
With In-Market Audiences, you can identify customers who are actively looking at products or services similar to yours.
Running with the same example, these might be customers who have added vegan recipe books to their shopping cart while browsing a website, or those who have browsed numerous sites related to running veganism.
You can target audiences on the display network to narrow your reach based on other, more diverse targeting methods which can be achieved via:
Placement targeting
Placement targeting refers to the choice of selecting which websites you want to appear on, allowing you the most power over where on the GDN you will appear.
This is productive for targeting a particular demographic and offers an incentive for advertisers to search for websites targeted to special interests that closely match their target audience.
So, if there are any industry-specific websites and forums that you feel are relevant and talk or write about products or services relevant to your business, we encourage you to engage in placement advertising with them for more impressions.
Contextual targeting
This is the most common targeting type since it utilises the keywords related to the products and services you offer.
You will first need to create a keyword list, and Google will do their best to display your ads on sites related to the keywords you’ve provided.
Instead of trying to come up with likely search queries like you would do for a search network campaign, you should be writing a list of 5-20 words or short phrases that are very closely related to the subject of your Ads.
Topic targeting
Topic targeting allows you to choose from an existing list of page topics, meaning that your ads will only display on pages about that topic.
The downside is that you can’t really dig into all of the topics too deeply, which means that there is a chance that your ads may appear on unrelated pages.
For example, a topic may be as wide-ranging as “food” whereas your ad could be highly targeted at the keyword “nutritious diet”.
With this in mind, to ensure that your ads are super targeted and important to the users who experience them, I would always recommend combining topical targeting with another targeting tool.
Remarketing
If you want to see a great return on the display network, remarketing is the first place you should start.
Remarketing allows for previous visitors to be targeted and followed up with via ads after they’ve initially visited your website.
Remarketing targeting varies from the very basic, meaning you’d be able to display advertisements to far more sophisticated groups with complex interests as well as to someone who has already visited your site.
For example, Google allows you to target your advertising specifically to individuals who have watched a video on your website and have stayed on the platform for a certain period of time.
The more remarketing lists you are able to set up, the more strategic you can be when using the display network to reach your audience.
It works because the people you’re remarketing to have already demonstrated a genuine interest in what you have to offer, by visiting your site.
The best thing about remarketing with the GDN is that it is very convenient and you can get very granular!
For example, Google lets you target your ads purely to people who stayed on your website for more than X minutes.
You can set up multiple remarketing lists based on different actions people took on your site, the products or content they’ve shown interest in, and more.

This is an example of a remarketing ad and strongly urges the viewer (with a CTA) to download the app.
Retargeting ads are for WARM traffic, but network display ads can also be incredibly powerful for COLD traffic interaction.
Combining Targeting Methods
If you apply more than one targeting approach to an ad category, your advertising will only be displayed to individuals who meet BOTH targeting requirements.
So, while you’ll get fewer impressions for your ads, you’ll know your ads are shown to people who really fit your ideal customer profile.
For example, you could use Topic + Interest Targeting.
So, if a user visits a site within the topic you select, AND they’re also in a matching interest category, you know the user consistently reads that type of content.
So, you have a higher chance of engaging the right type of visitor than if you used either topic or interest alone.
Optimising The Display Ads Campaign
How can you make sure you’re getting the absolute best return from your display ad campaigns?
You need to give the same love you would give search ads to your show campaigns (or any other digital channel).
Take time to review their performance on a regular basis, especially if you are using the automatic placements.
A primary method to study and optimise display campaigns is to regularly review the automatic placements report. You can support this by adding strong performing placements to managed placement campaigns.
It is also advised that you add any irrelevant or poor performing sites as negative placements in your automatic placement campaign.
Other optimisation techniques for display network campaigns include:
Excluding irrelevant categories
These may include certain specific placements that don’t fit your brand or placements where your ads are showing, and are not performing well.
Example:
A travel agency has an ad group that features family water park activity packages and targets topics like Outdoor Activities.
The agency notices that some of their ads are showing up on automatic placements that are relevant to the topic but are not family-friendly.
They can exclude those placements from the ad group.
To do this:
- Sign in to your Google Ads account.
- From the page menu on the left, select Placements.
- From the menu bar on the left, click the Exclusions tab.
- Click the pencil icon.
- Choose whether you’d like to exclude placements at the campaign, ad group or account level.
- Search for a word, phrase, URL or video ID that you’d like to exclude.
- Click Enter multiple placements and enter the URL(s) that you’d like to exclude.
- Select Use placement exclusion list and select your list.
- After you’ve entered your exclusions, click Save.
Excluding irrelevant audiences
Bear in mind that audience exclusions are only available in certain campaign types:
“Discovery campaigns”
“Display Network only” > “Marketing objectives” > “Drive action” > “Buy on your website”
“Display Network only ” > “No marketing objective” > “All features”
“Display Network only – Remarketing”
“Display Network only – All features”
“Search Network with Display Select – All features”
“Search Network only – All features”
“Search Network only – Dynamic Search Ads”
To exclude audiences at the ad group and campaign level:
- Sign in to your Google Ads account.
- Click on Audiences.
- Click Exclusions.
- Click the audience exclusions icon (a plus sign on a blue button)
- Select “Campaign” or “Ad group” from the drop-down.
- Select “Affinity audiences”, “In-market audiences” or “Remarketing and similar audiences”.
- Click “Affinity audiences”, “In-market audiences” or “Remarketing and similar audiences”.
- Select as many specific audiences as you would like to exclude, either by using “Search” or by clicking the box next to each audience. Your audience will appear in the “Selected” column.
- Click Save.
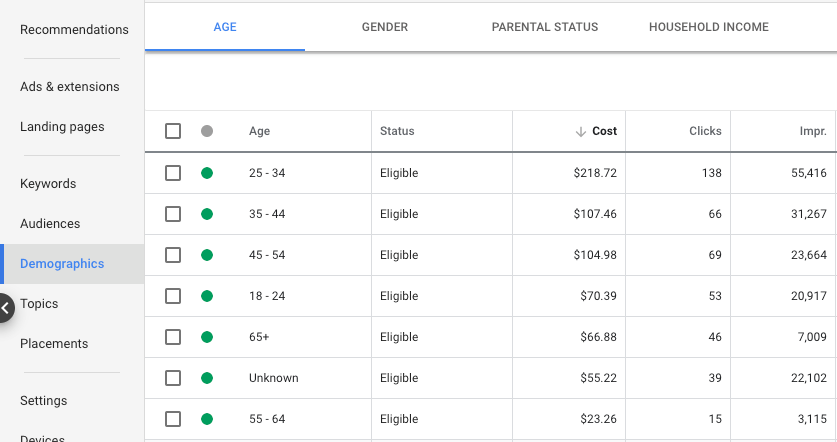
Reviewing Ad Results Based on Demographic Performance
Some of your audience’s demographics might be perfect for conventional marketing, but they may perform poorly in a digital environment.
It is important to check the output of what has not been excluded, even after setting up unique demographic and location targeting.
Adding click-to-call extensions
If you are targeting mobile devices, call extensions allow you to add phone numbers to your ads. These can significantly increase click-through rates.
When your call extensions are displayed, people may click a button to directly call your business.
That means more customer contact with your advertising and more chances for you to get your conversions and track them.
Google Ads may set up automated call extensions when your website has a phone number, and your business goals include getting people to call you.
Exclude Mobile Apps
Mobile apps probably won’t be useful for you to include your ads in games and music apps.
In order to quickly return to the game, most individuals mistakenly click on the ads. Rather than making a purchase or finding B2B services, they’re trying to amuse themselves. On these accidental clicks, avoid wasting money.
To do this:
1. Go to your Google Ads dashboard, select the “Placements” tab, then click to “Exclusions.”
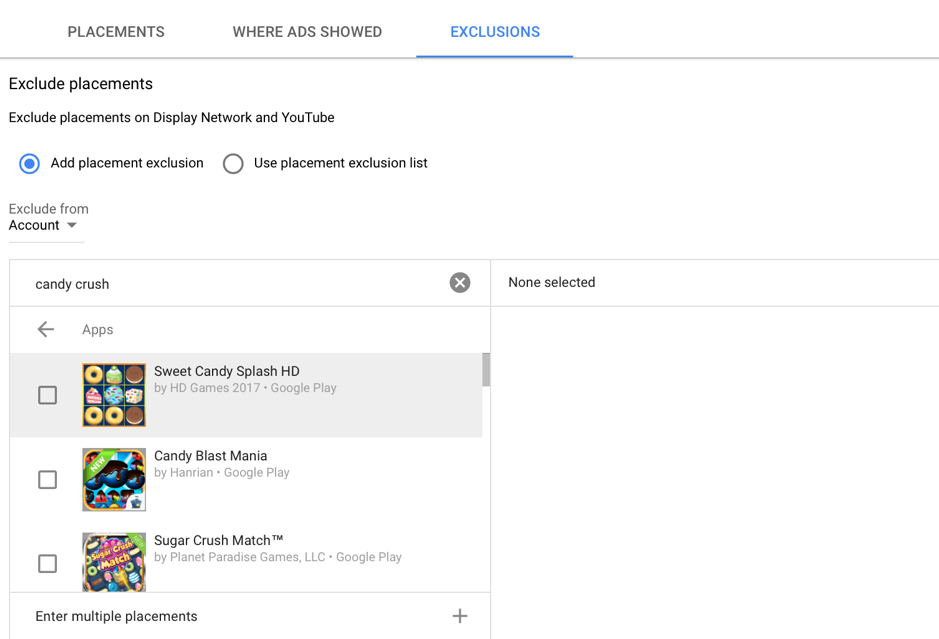
2. Click “Add placement exclusion”, then enter the names of any apps or sites you want to omit.
3. In addition to the big ones, go to Google Analytics to see if other apps are sending you a high amounts of clicks.
Other strategies
You can implement many strategies to continuously increase the efficacy of your display network ventures.
But if you are just starting on the Display Network and want to track performance closely on specific sites, then you should spend your time regularly reviewing your placement reports.
Google makes it easy to review where your ads are appearing on a daily or weekly basis after campaign launch.
You can find this information under “Placements > Where Ads Showed”.
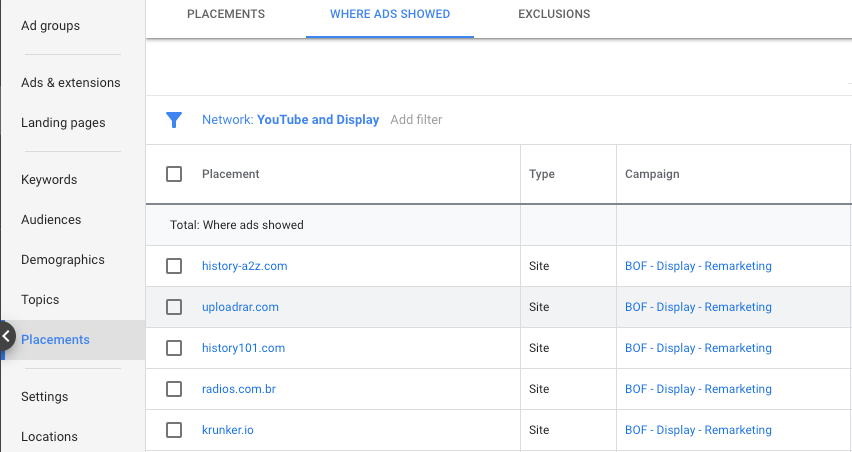
Websites that are more of an imminent threat to the health of your campaign can be easily detected by filtering placements from excessively high spending or CTR.
If you consider bulk exclusions, you might find it useful to export site placements within the “all-time” period.
Focus on blocking duplicate placements that generate no effects, as repeat offenders are a higher priority than websites with just a few impressions that appear once.
Check the usefulness of these sites after finding duplicates, how much they have invested, and whether they have contributed to any conversions.
Ad style and Location
There are two main ad types available for a GDN campaign – standard image ads and responsive ads.
There are a variety of formats, including rectangle, rectangular, skyscraper, and banner, for standard picture advertising.
These advertisements are a choice for a picture-only show. An example is shown below:

On the other hand, responsive ads offer a combination of text and image options that display in a variety of formats, depending on where the ad appears.
Three picture styles, up to five short headlines, one long headline, up to five explanations, and a company name make up the full commercial.
To find the best-performing mix, the brief headlines and explanations rotate. An example is here:
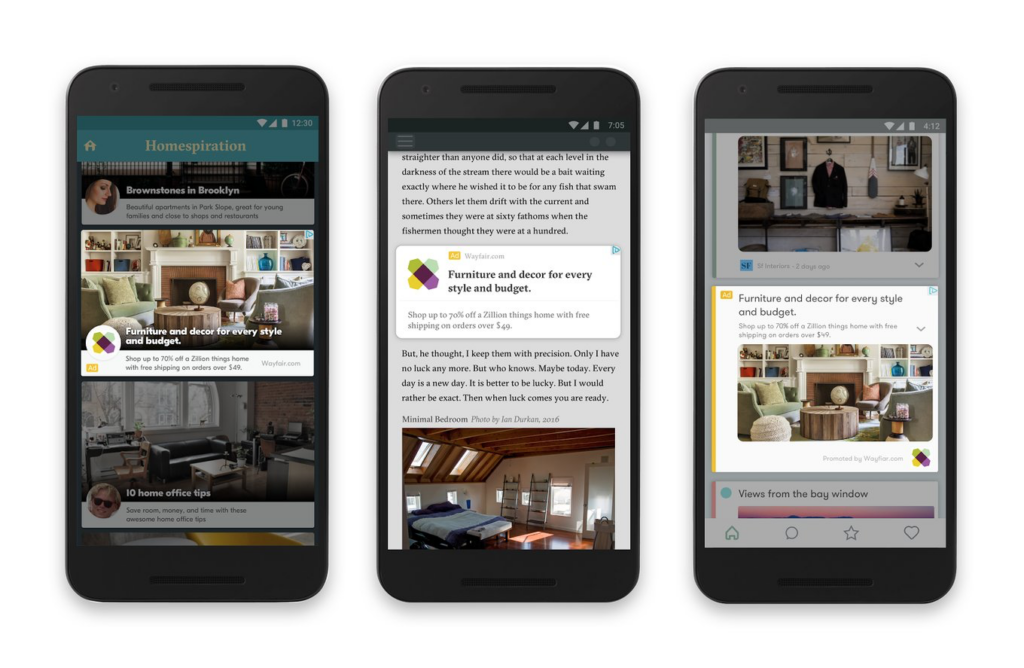
If you’re limited in time, budget, or creative capital, knowing which display advertising would work better for your campaign can be challenging, and you may not want to risk testing various ads over time.
It is important to remember if this is the case that studies have shown that 300 x 250 and 728 x 90 get more impressions than other ad formats.
Half-page advertising and large rectangles often receive greater CTRs than other formats of ads. So if you’re not sure where to start, check out the leaderboards and rectangular formats:

Top Sectors For Display Advertising
For most firms, display ads can be used to improve paid results.
Indeed, the search network can be so competitive in some sectors that the display network offers the best chance for smaller companies to gain paid online exposure.

As you can see, gambling and finance dominate the list of the most costly keywords, and you can see real estate, business services and, predictably, advertising further down the list!
So you might benefit from attempting to advertise on the Display Network if your company falls into any of these categories and your advertising budget is low.
In reality, even if you don’t fall into these categories, you might still want to try our campaign alongside a search network as it’s so much cheaper.
Conclusion
That’s all folks!
That covers pretty much everything you need to get started on the right track towards launching a successful Google Ads campaign on the Google Display Network.
Remember to do your due diligence; the difference lies in your research which is, ultimately, going to give you your competitive edge.
More importantly, keep your budgeting in check!
It is very easy to get lost in the plethora of options Google provides. So make sure you monitor every aspect of your campaigns yourself – from placement target impressions to the size of your display ad.
However, if you feel like you still need a pair of eyes to make sure you’re all set, we are here to help!
Book a call with our team of professionals here, and we can get your campaign fired up!