Keeping an eye on Google Search Console is a must when you own or run a website of any kind, and any errors encountered while doing so can be frustrating, especially if you are not quite sure what they mean or how to fix them. for example, if a Google notification states ‘submitted URL marked ‘noindex’, what do they mean? What are the implications for your website (and its SEO) and just how do you fix a ‘submitted URL marked ‘noindex’ error. These issues and more are what we are going to take a closer look at now.
What Does the Submitted URL Marked ‘noindex’ Error Mean?
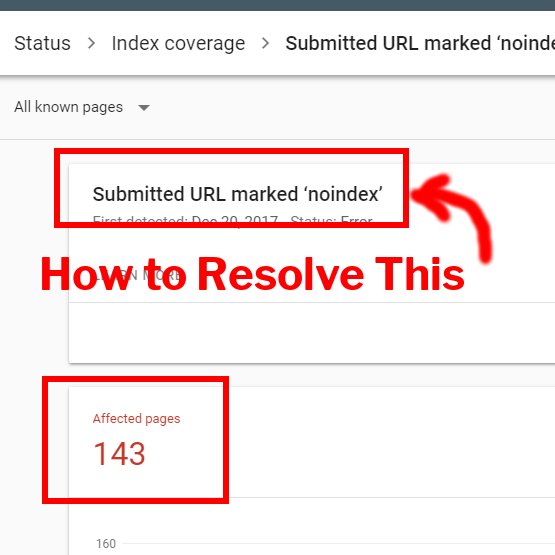
In a nutshell, the page in question – the error will be attached to page link is not indexed, as indicated by the word “error.”
In other words, Google attempted but failed to index your page. Why is that? On the one hand, the term “submitted URL” denotes that the page has been submitted to Google for indexing. This implies that the URL has been added to a sitemap that Googlebots have attempted to follow during a crawl of your site.
On the other hand, something on the page is preventing Googlebot from indexing it. A noindex meta tag in the page’s source code or an X-Robots-Tag HTTP header might have been used.
As a result, the page will not appear in the results of a search. Confused, the Googlebot tasked with following a sitemap that then throws up a roadblock triggers this error alert in Google Console.
How to Fix the ‘submitted URL marked noindex’ Error
How you go about fixing this error very much depends on what you really want the Googlebot to do.
If you do want it to index the page, then you have to remove whatever is preventing it from crawling the page, so it can do so. With that in mind here’s a closer look at the process to fix the ‘submitted URL marked noindex’ error if and when it shows up in your Google Console.
Verify Live URLs
Examine the list of pages from the report to see if they are still listed in the XML sitemap and whether they are marked as noindex. To make sure you’re looking at the most recent version of your site as you follow links from the Google Console report to your site, clear the cache before you do so.
You can do this manually if there are only a few URLs, simply clicking on each link in the report. If there are lots of URLS included you might want to make use of a link checking utility, which will do much of the work for you and present you with a list of ‘trouble’ links.
The First Fix
As a result of the verification process we just described you’ll end up with two possible outcomes.
Pages that have been deliberately tagged with the noindex attribute are incorrectly included in the XML sitemap: you’ll need to remove these pages from the XML sitemap.
Pages that are incorrectly marked noindex and included in the XML sitemap should have their indexability status updated, and you should be good to go.
Why Would You Mark Pages ‘noindex’ in the First Place?
Some of your site’s pages have a purpose, but it isn’t to improve your search engine rankings or drive traffic to your site. These pages are required to be accessible on your website, either as a glue for other pages or because of regulations that govern your website in the jurisdiction it operates in.
Which might these pages be? Here are some examples:
Single Author Archives
If you’re the only person who writes for your blog, your author pages are almost certainly identical to your blog’s homepage. This is irrelevant to Google and could even be considered duplicate content. You can choose to turn off the author archive entirely to avoid duplicate content or you can noindex it if you want to keep it on your site but out of the search results.
Certain Types of (custom) Posts
A plugin or a web developer might create a custom post type that you don’t want indexed. You can either delete them or noindex them if they serve a purpose – which is often the case for e-commerce sites.
Thankyou Pages
Usually a thankyou page’s sole purpose is to express gratitude to your customer, newsletter subscriber, or first-time commenter. These are usually thin content pages with upsell and social share options, but no value for someone looking for information on Google. As a result, those pages should not appear in the search results.
Login and Admin Pages
The majority of login pages should not be found in Google. Add a noindex to yours to keep it out of the index. The login pages that serve a community are an exception. If you are not sure if you should noindex a login page or not, simply ask yourself if you, as a browser/customer/consumer, would Google one of your login pages. If not, it’s safe to assume that Google should not be indexing these login pages.
How to Remove/Add a noindex Value
Different CMS platforms offer different ways to add or remove a noindex tag, and some have plugins that make it easier. WordPress, for example, can be used with several plugins – the most prominent being Yoast – that will walk you through doing this as a part of plugin set up, and some WordPress themes have an option in the composition of interface of pages and posts that you can simply check to mark your work noindex.
If you do need or want to look for the meta tag in the page’s source code, look for something that looks like this: meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”> meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”> You should also look for a noindex, noarchive, or other negative header in your HTTP headers.
Removing a URL from a Sitemap
If you did mean to mark page noindex, but did not mean to include it in an XML sitemap you’ll need to generate a new sitemap that does not include that URL. How you do that will depend on how your sitemap is generated. Most websites make use of a plugin or special utility of some kind. Go through its settings to ensure that the pages it is going to submit are actually the ones you want there.
How to Fix the ‘submitted URL marked noindex’ Error with Google
Once you have fixed the error, you’ll need to tell Google about it, in order to trigger a recrawl by their Googlebot. To do this you’ll need to use the URL inspection tool in Google Search Console so that Google can check your work. If you have never used this tool before, this video from the company themselves does an excellent job of explaining how.
faqs
If you notice a submitted URL marked ‘noindex’ check to see if the page is private, password protected, or only available for certain members.
If you noticed a google search console noindex error then Google has decided that your page can not be indexed and taken public.
If your url is marked noindex, try clearing your cache and make sure your WordPress is updated. Then verify if your pages are listed in the XML sitemap.